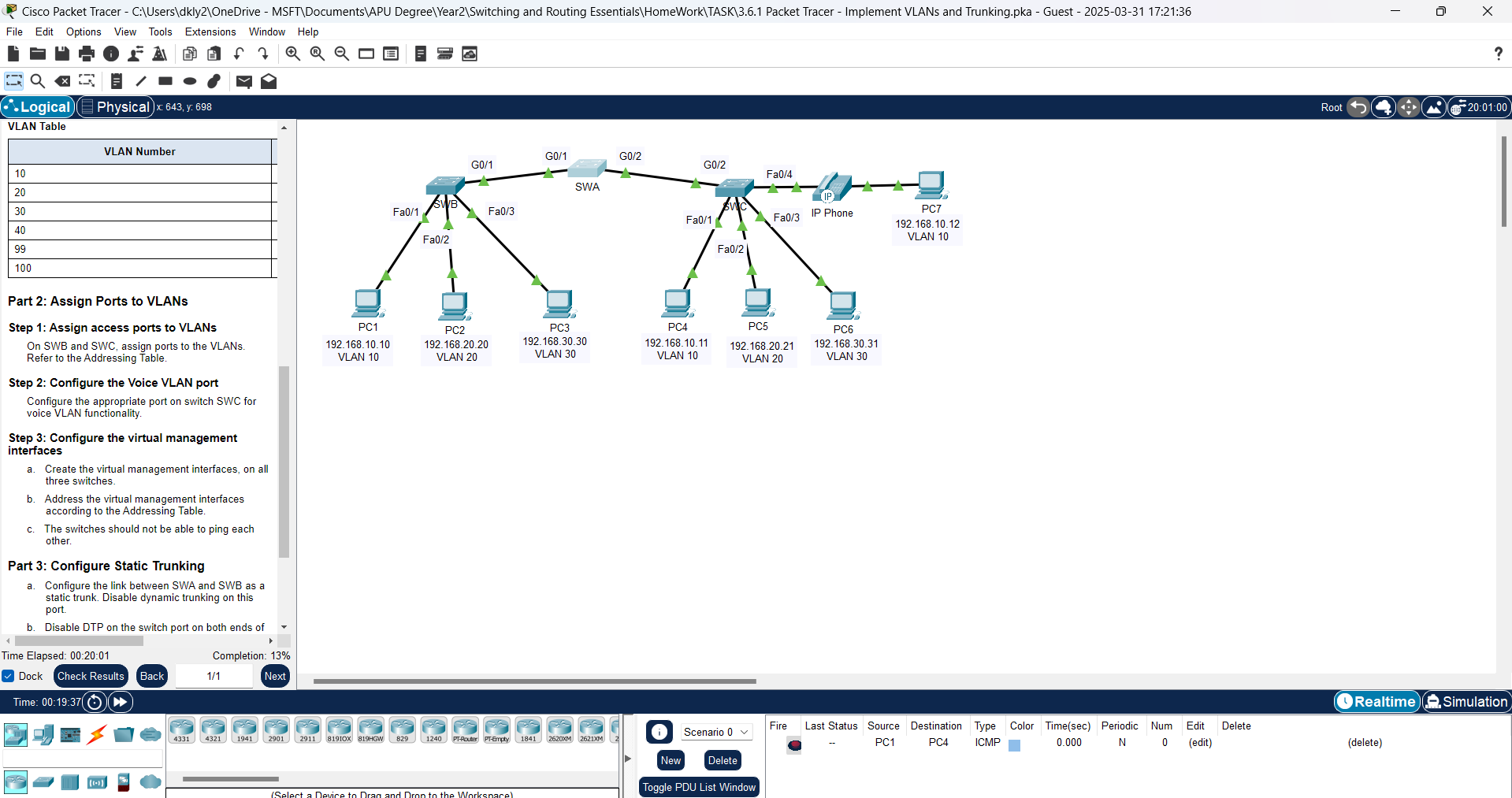
In modern networking, Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) and trunking play a crucial role in segmenting networks and ensuring efficient communication between different departments or devices. VLANs allow network administrators to logically separate traffic within a switch, improving security, performance, and manageability. Trunking, on the other hand, enables VLAN communication across multiple switches, ensuring seamless connectivity. In this Packet Tracer activity, we will implement VLANs, assign ports, and configure trunk links to create a well-structured and efficient network.
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Switchport | VLAN |
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.10.10 | 255.255.255.0 | SWB F0/1 | VLAN 10 |
| PC2 | NIC | 192.168.20.20 | 255.255.255.0 | SWB F0/2 | VLAN 20 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.30.30 | 255.255.255.0 | SWB F0/3 | VLAN 30 |
| PC4 | NIC | 192.168.10.11 | 255.255.255.0 | SWC F0/1 | VLAN 10 |
| PC5 | NIC | 192.168.20.21 | 255.255.255.0 | SWC F0/2 | VLAN 20 |
| PC6 | NIC | 192.168.30.31 | 255.255.255.0 | SWC F0/3 | VLAN 30 |
| PC7 | NIC | 192.168.10.12 | 255.255.255.0 | SWC F0/4 | VLAN 10 VLAN 40 (Voice) |
| SWA | SVI | 192.168.99.252 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | VLAN 99 |
| SWB | SVI | 192.168.99.253 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | VLAN 99 |
| SWC | SVI | 192.168.99.254 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | VLAN 99 |
Background
You are working in a company that is getting ready to deploy a set of new 2960 switches in a branch office. You are working in the lab to test out the VLAN and trunking configurations that are planned. Configure and test the VLANs and trunks.
Instructions
Part 1: Configure VLANs
Configure VLANs on all three switches. Refer to the VLAN Table. Note that the VLAN names must match the values in the table exactly.
VLAN Table
| VLAN Number | VLAN Name |
| 10 | Admin |
| 20 | Accounts |
| 30 | HR |
| 40 | Voice |
| 99 | Management |
| 100 | Native |
Solutions: Configure these in Switch 1 (SWA), Switch 2 (SWB), Switch 3 (SWC)
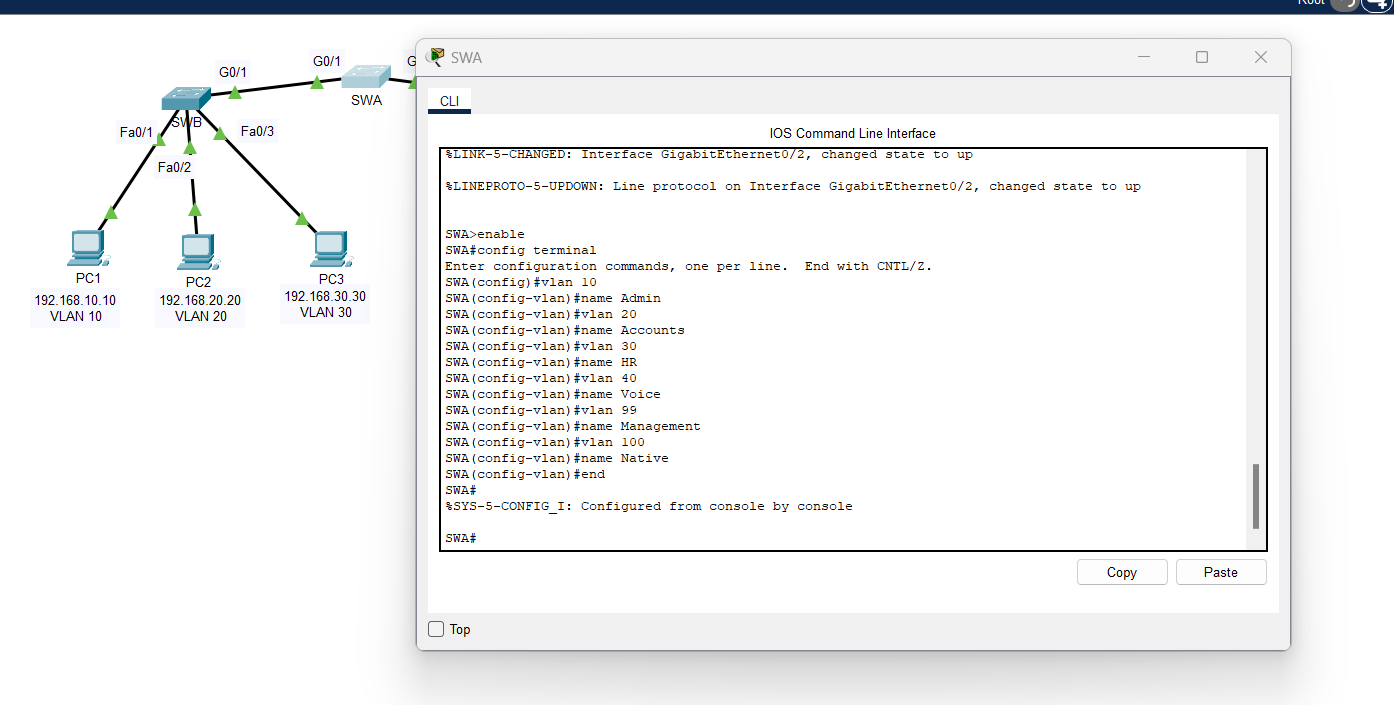
| SWA>enable
SWA#config terminal SWA(config)#vlan 10 SWA(config-vlan)#name Admin SWA(config-vlan)#vlan 20 SWA(config-vlan)#name Accounts SWA(config-vlan)#vlan 30 SWA(config-vlan)#name HR SWA(config-vlan)#vlan 40 SWA(config-vlan)#name Voice SWA(config-vlan)#vlan 99 SWA(config-vlan)#name Management SWA(config-vlan)#vlan 100 SWA(config-vlan)#name Native SWA(config-vlan)#end |

Part 2: Assign Ports to VLANs
Step 1: Assign access ports to VLANs
On SWB and SWC, assign ports to the VLANs. Refer to the Addressing Table.
Solutions:
1) Switch 2 (SWB):
| interface f0/1
switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 interface f0/2 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 20 interface f0/3 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 30 |
2) Switch 3 (SWC):
| interface f0/1
switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 interface f0/2 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 20 interface f0/3 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 30 interface f0/4 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 |
Step 2: Configure the Voice VLAN port
Configure the appropriate port on switch SWC for voice VLAN functionality.
Solutions:
| interface f0/4
mls qos trust cos switchport voice vlan 40 |
Step 3: Configure the virtual management interfaces
a. Create the virtual management interfaces, on all three switches.
Solutions:
| SWA>enable
SWA#config terminal SWA(config)#int vlan 99 %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Vlan99, changed state to up SWA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.252 255.255.255.0 SWA(config-if)#no shutdown SWA(config-if)#exit SWA(config)#int vlan 99 SWA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.253 255.255.255.0 SWA(config-if)#no shutdown SWA(config-if)#exit SWA(config)#int vlan 99 SWA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.254 255.255.255.0 SWA(config-if)#no shutdown SWA(config-if)#exit |
2) Switch B (SWB):
| SWB>enable
SWB#config terminal SWB(config)#int vlan 99 %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Vlan99, changed state to up SWB(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.252 255.255.255.0 SWB(config-if)#no shutdown SWB(config-if)#exit SWB(config)#int vlan 99 SWB(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.253 255.255.255.0 SWB(config-if)#exit SWB(config)#int vlan 99 SWB(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.254 255.255.255.0 SWB(config-if)#no shutdown SWB(config-if)#exit |
3) Switch C (SWC):
| SWC>enable
SWC#config terminal SWC(config)#int vlan 99 %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Vlan99, changed state to up SWC(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.252 255.255.255.0 SWC(config-if)#no shutdown SWC(config-if)#exit SWC(config)#int vlan 99 SWC(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.253 255.255.255.0 SWC(config-if)#no shutdown SWC(config-if)#exit SWC(config)#int vlan 99 SWC(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.254 255.255.255.0 SWC(config-if)#no shutdown SWC(config-if)#exit |
b. Address the virtual management interfaces according to the Addressing Table.
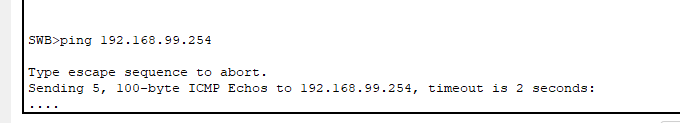
c. The switches should not be able to ping each other.
Part 3: Configure Static Trunking
a. Configure the link between SWA and SWB as a static trunk. Disable dynamic trunking on this port.
b. Disable DTP on the switch port on both ends of the trunk link.
c. Configure the trunk with the native VLAN and eliminate native VLAN conflicts if any.
Solutions:
1) Switch A (SWA):
1) Switch A (SWA):
| SWA(config)#interface g0/1
SWA(config-if)#switchport mode trunk SWA(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate SWA(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 100 |
2) Switch C (SWC):
| SWB(config)#interface g0/1
SWB(config-if)#switchport mode trunk SWB(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate SWB(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 100 |
Part 4: Configure Dynamic Trunking
a. Assume that the trunk port on SWC is set to the default DTP mode for 2960 switches. Configure G0/2 on SWA so that it successfully negotiates trunking with SWC.
b. Configure the trunk with the native VLAN and eliminate native VLAN conflicts if any.
Solutions:
1) Switch A (SWA):
1) Switch A (SWA):
| SWA(config)#interface g0/2
SWA(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic desirable |
2) Switch C (SWC):
| SWC(config)#interface g0/2
SWC(config-if)#switchport mode trunk SWC(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 100 |
By successfully implementing VLANs and trunking in Packet Tracer, we have demonstrated how to segment networks effectively and enable communication between different VLANs using trunk links. These configurations are essential in real-world networking, especially in enterprise environments where network efficiency and security are paramount. Understanding VLANs and trunking is a fundamental step toward mastering Cisco networking and preparing for CCNA certifications. Keep practicing with Packet Tracer to reinforce these skills and enhance your networking expertise!